Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that generally involves damage to the optic nerve and loss of vision due to damage to the visual field. This condition can result from high intraocular pressure or even arise when the intraocular pressure is within normal limits.
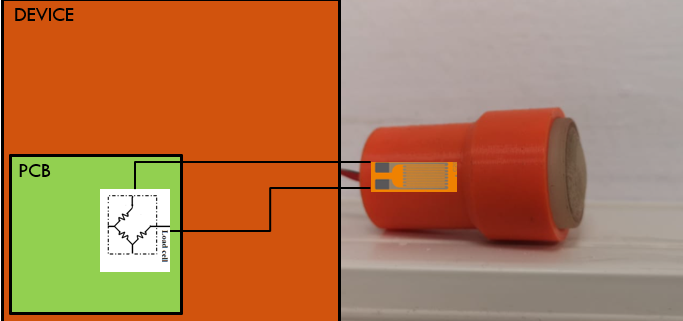
This project implemented a Glaucoma indicator device prototype using two sensors (force and pressure) to predict the intraocular pressure.
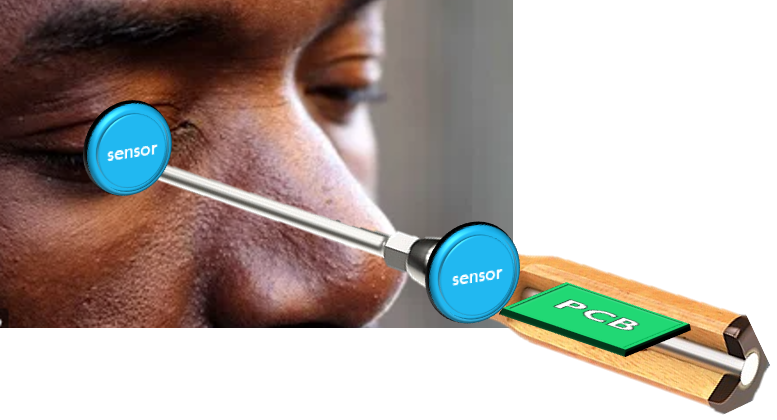
In third world countries, there is low accessibility for doctors in general and ophthalmologists in particular, thus there is a need for a portable and inexpensive device that allows self-examination to detect glaucoma early, indicating the need for further evaluation.
In this project, two sensors were used (force and pressure) to predict intraocular pressure:
By applying pressure to a closed eye, the pressure sensor measures the change in electrical resistance.
The force sensor is used to measure the power implicated by the user.
These two measurements, and a large number of others, could be combined to form a database, which would serve as a starting point for future work.
The implementation involved PCB design, “bring up” and software development. Bluetooth is used for transmitting the data received by this device to other Bluetooth devices.
As the main action of the project, a series of measurements begins as soon as a threshold has been reached.