An acousto-optic imaging (AOI) algorithm for real-time deep tissue imaging is implemented, transitioning from MATLAB to hardware-compatible C code to meet real-time processing and resource constraints. By optimizing computational efficiency and managing high data flow rates, the validated implementation accurately reconstructs tissue layers and demonstrates its feasibility for future AOI systems.
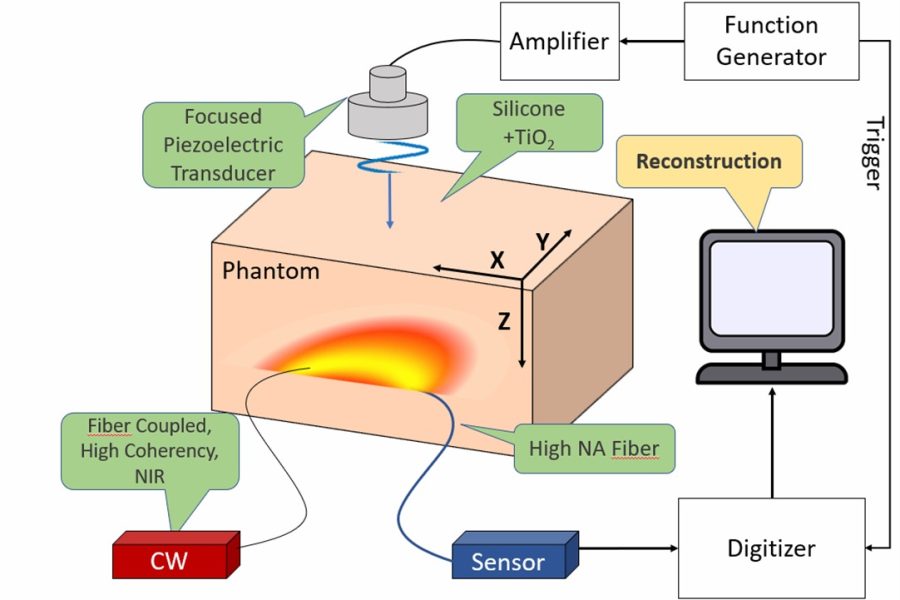
This project focuses on the implementation of an acousto-optic imaging (AOI) algorithm for multichannel analysis,
aimed at real-time deep tissue imaging.
AOI is a hybrid technique that combines laser illumination and ultrasonic modulation to map the internal optical properties of tissues.
The algorithm was initially developed in MATLAB and transitioned to a hardware-compatible implementation in C,
designed to meet the requirements of real-time processing and resource constraints.
Key aspects of the project include handling high data flow rates from multichannel acquisition systems,
optimizing computational efficiency through fixed-point arithmetic,
and replacing floating-point operations to align with hardware capabilities.
The implementation was validated using experimental data, demonstrating accurate reconstruction of tissue layers by extracting light fluence rates.
The results confirm the algorithm’s feasibility for real-time applications and its potential for future use in acousto-optic imaging systems.


