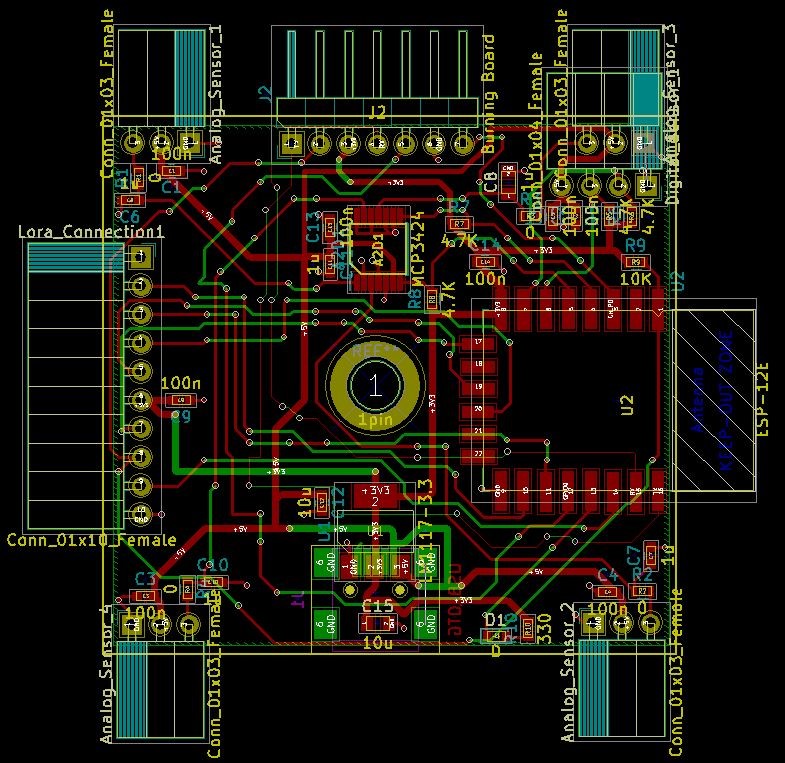
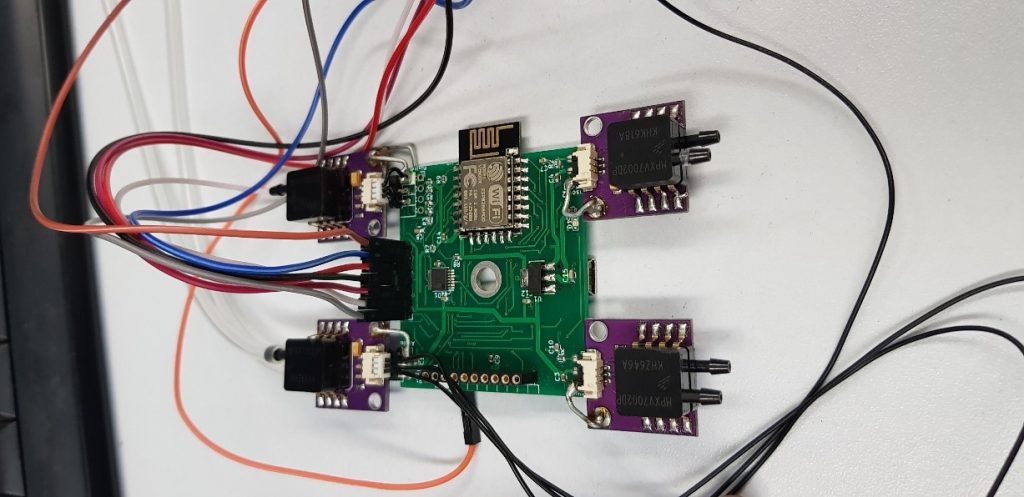
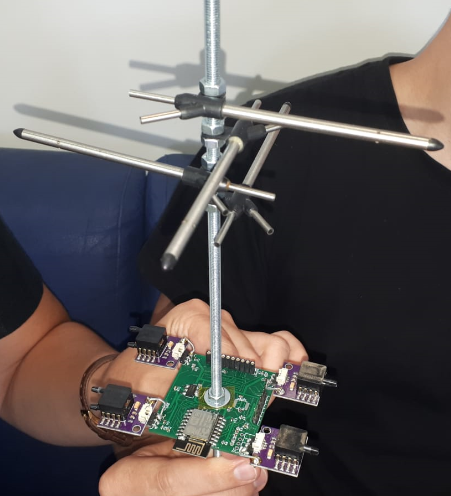
Anemometers (wind speed meters) are an important measurement tool that have several applications in a variety of fields. They have moving parts that cause erosion and increase the physical size of the component. The project’s main goal is to make a cluster of IOT-sensors (without moving parts) that will replace the traditional anemometers. In addition the cluster will show both the wind speed and wind direction in the location that they have been placed at.
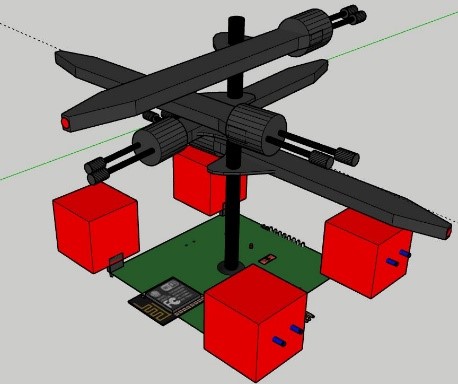
Anemometers (wind speed meters) are an important measurement tool that have several applications in a variety of fields, for example to measure microclimate. As of today, all the anemometers are based on a weather vane and have moving parts that cause erosion and increase the physical size of the component. High price and robust physical structure, disqualified the anemometer from being the best solution to the problem.
Therefore, a dedicated IOT-sensor is intended to replace the anemometer. The IOT-sensors design is inspired by the design and workflow of the pitot tube. A pitot-static system is a system of pressure-sensitive instruments that is most often used in aviation to determine an aircraft’s airspeed, altitud e and more. The innovation in this system is the convergence of air pressure (dynamic and static) to airspeed. In our project, each IOT-sensor has four pitot-tubes, in order to determine wind-speed in every direction.

The IOT enables the cluster to share information to the cloud. In addition, the sensor measures the velocity and direction of the wind without any moving parts in order to maximize its reliability. The IOT-sensor will also be autonomous and use only solar energy. Thus, it may be stationed anywhere without interfering the environment.